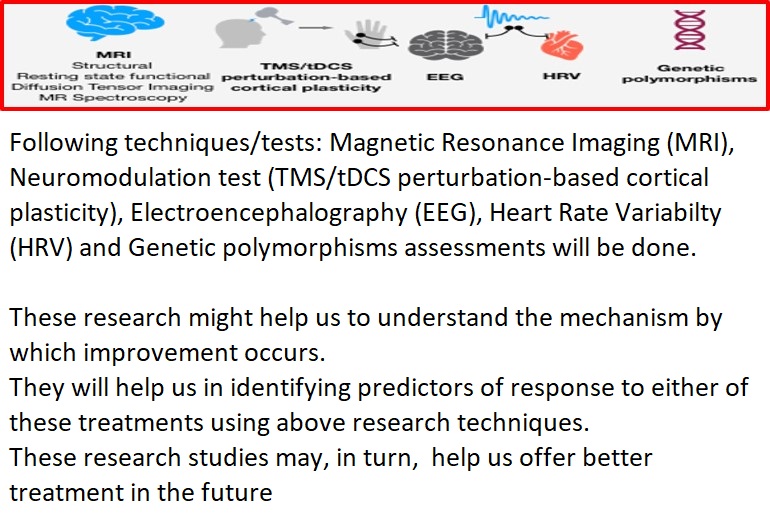
Introduction to Study:
The study examines clinical benefits and mechanisms of two steps of treating individuals with depression who have not responded well to earlier treatment.
Step 1: The first step of treatment uses neuromodulation therapies like iTBS and c-tDCS (see details in information booklet).
Step 2: The second step of treatment is with electroconvulsive therapy or ECT, when there is insufficient response in the first step.
Previous research studies have shown that individuals with treatment-resistant depression/intolerance to antidepressant medications may respond to a brain stimulation technique called “intermittent theta-burst stimulation (iTBS)” – an advance type of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). However, patients respond differently (i.e., some individuals respond well, and some do not) to these neuromodulation treatments and currently, we are unable to predict which patient will respond to iTBS treatment. Also, combining iTBS with another neuromodulation technique called “cathodal transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (c-tDCS) might result in a better treatment response.
The purpose of this research study is to compare iTBS treatment (i.e. iTBS alone) with iTBS combined with c-tDCS treatment (i.e. iTBS + c-tDCS) in terms of their efficacy in improving the depression.
![]() Information Booklet – Brain Stimulation for Resistant Depression
Information Booklet – Brain Stimulation for Resistant Depression